Our Approach
Q32 Bio is targeting dysfunctional regulation of both the innate and adaptive immune systems so that homeostasis can be restored across a diversity of organ systems and disease indications.
Targeting IL-7
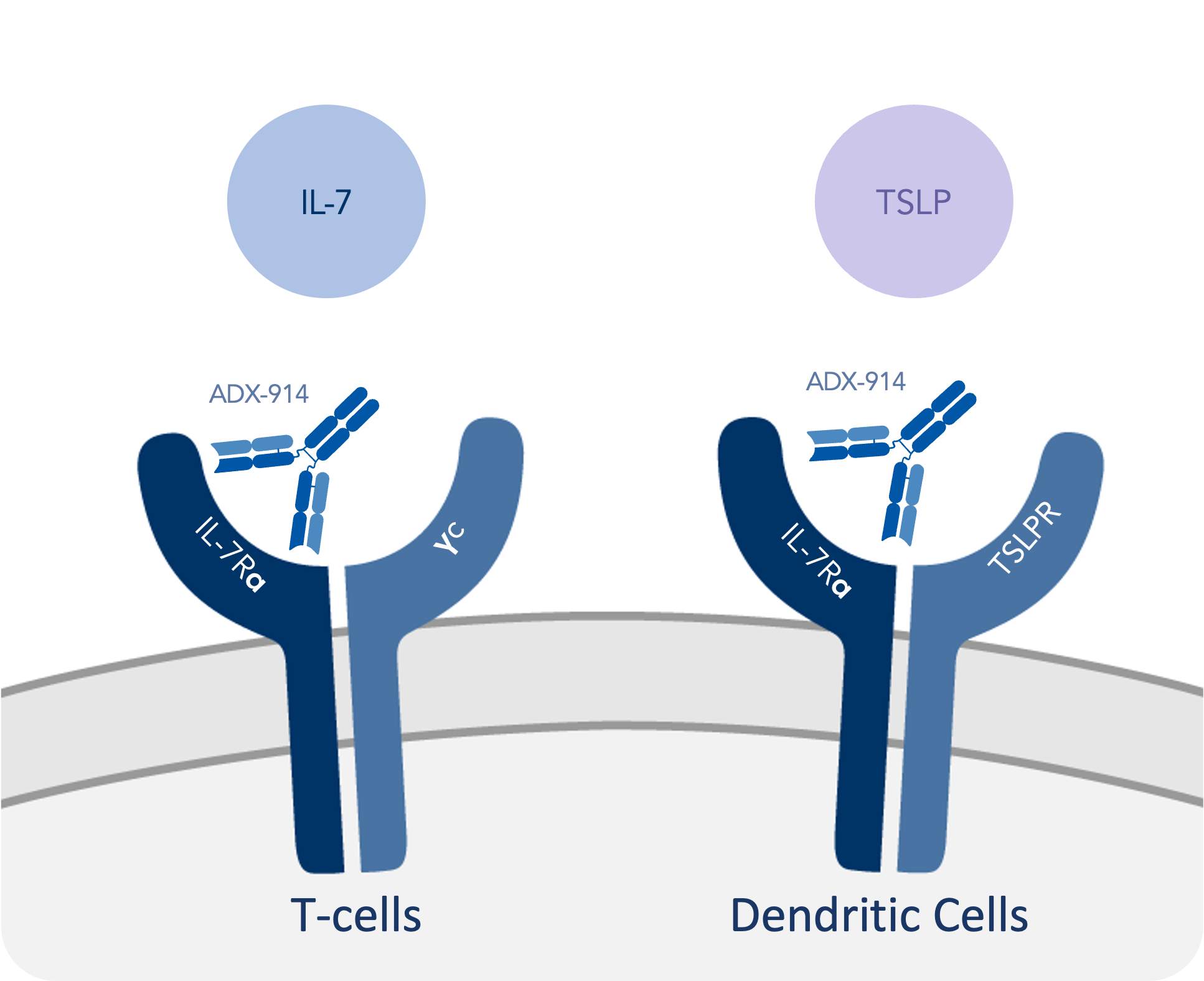
Bempikibart (ADX-914), Q32 Bio’s most advanced product candidate, is a fully human anti-IL-7 receptor alpha (IL-7Rα) antibody that is designed to re-regulate adaptive immune function by blocking IL-7 and TSLP signaling, both of which contribute to inflammation and injury in a diversity of autoimmune disorders.
IL-7 is a cytokine that maintains the proliferation and survival of autoreactive T-effector cells and lowers their threshold for response in low antigen microenvironments. When these pathogenic T-effector cells expand and become activated they interfere with the immunosuppressive function of T-regulatory cells. As a result, it is believed that IL-7 has the potent ability to promote and sustain inflammation and autoimmunity in multiple diseases.
TSLP is an epithelial-cell-derived cytokine that promotes inflammation in response to environmental stimuli. It is critically important for mediating Type 2 allergic immunity at barrier surfaces and has been implicated in several inflammatory and allergic conditions. Therefore, antagonism of the TSLP receptor has the potential to effectively treat a diverse group of diseases, including those in which both the IL-7 and TSLP pathways play a role in the disease pathogenesis together, in an overlapping manner, or sequentially.
For patients with a wide range of autoimmune diseases, including atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata, Q32 Bio believes the blockade of IL-7 and/or TSLP signaling may offer a new therapeutic approach to modulate the autoimmune response. A high unmet medical need exists for more broadly effective therapies in these conditions, and Q32 Bio is developing bempikibart with the goal of addressing this need.
IL-7/TSLP ProgramOur Unique Approach to Complement
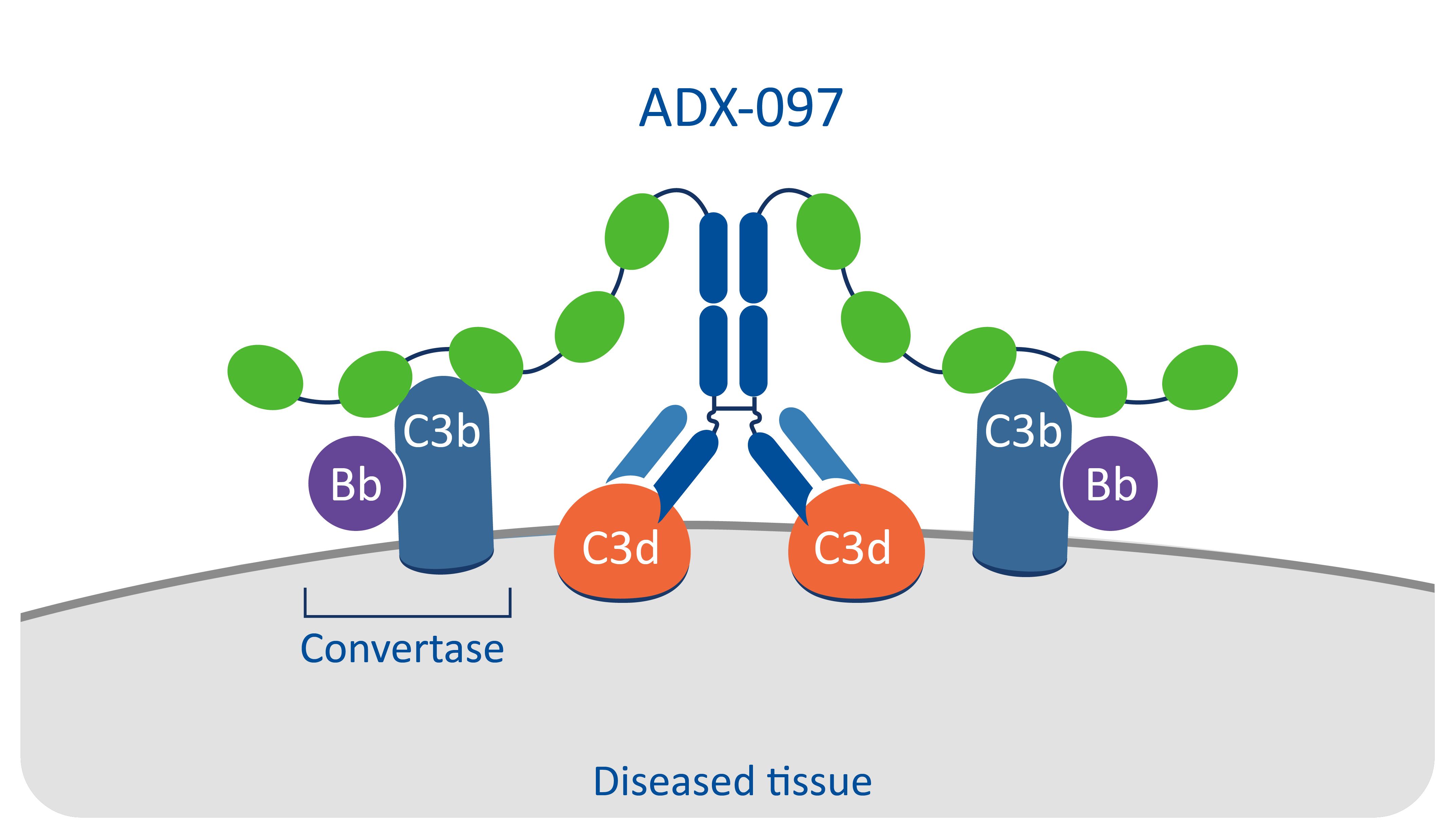
Complement regulation is an integral part of the innate immune system and provides important protective functions. The complement system can be activated through three pathways, in which component proteins such as Complement Component 3 (C3) undergo cleavage into smaller protein fragments. These protein fragments have multiple functions, including clearance of cell debris, elimination of pathogenic intruders and modulation of adaptive immunity. The complement system is tightly regulated by a broad tapestry of both positive and negative regulatory proteins. Disruption in the balance between complement activation and regulation can have pathological and potentially life-threatening consequences that derive from the complement system causing unrestricted and persistent tissue inflammation, cellular destruction and ultimately impaired organ function. The number of diseases associated with hyperactivation or dysregulation of the complement system is extensive and encompasses most major organ systems including the kidney, skin, blood, lung, neuromuscular junction and brain.
Q32 Bio is pioneering a platform underpinned by a new approach to treating complement-mediated diseases by targeting our drugs directly to the affected tissue, while allowing for the other important functions of complement to remain largely unimpaired.
The lead program from our tissue-targeted complement inhibitor platform is ADX-097. We believe ADX-097 has the potential to drive improved clinical activity and address the limitations of the currently available systemic approaches to complement inhibition, including infection risk and the need for high drug doses and frequent administration to achieve therapeutic levels of inhibition.

